Footnotes
(Note) An online tool developed by WWF and DEG, a German development financial institution, designed to support the identification, assessment, and response to water-related environmental risks (Source: WWF Japan).
Water Risk Assessment and Response
DAIICHI SANKYO COMPANY, LIMITED
| Update date | January 9, 2025(Posted on July 7, 2025) |
|---|---|
| Publication date | July 25, 2018 |
| Sector | Water Resources and Water Environment / Industry and Economy |
Company Overview

The Daiichi Sankyo Group is working to address unmet medical needs as an innovative pharmaceutical company with a strong focus on oncology. In the pursuit of becoming a "Global Pharma Innovator with Competitive Advantage on Oncology" the Group also provides a wide range of pharmaceutical products, including vaccines, generics, and over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, aiming to contribute to comprehensive healthcare solutions.
Climate Change Impacts
Possible impacts of climate change include tighter regulations on CO2 emissions based on the international framework for greenhouse gas reduction, physical impacts such as rising average temperatures, droughts and floods, and changes in disease patterns and public health risks. The Daiichi Sankyo Group considers the availability of sufficient supplies of high-quality freshwater at all of its sites and throughout its value chain to be critical for sustaining and advancing its business operations.
Adaptation Initiatives
The Daiichi Sankyo Group monitors the status of risks that may affect its business operations, focusing on its manufacturing plants and research laboratories.
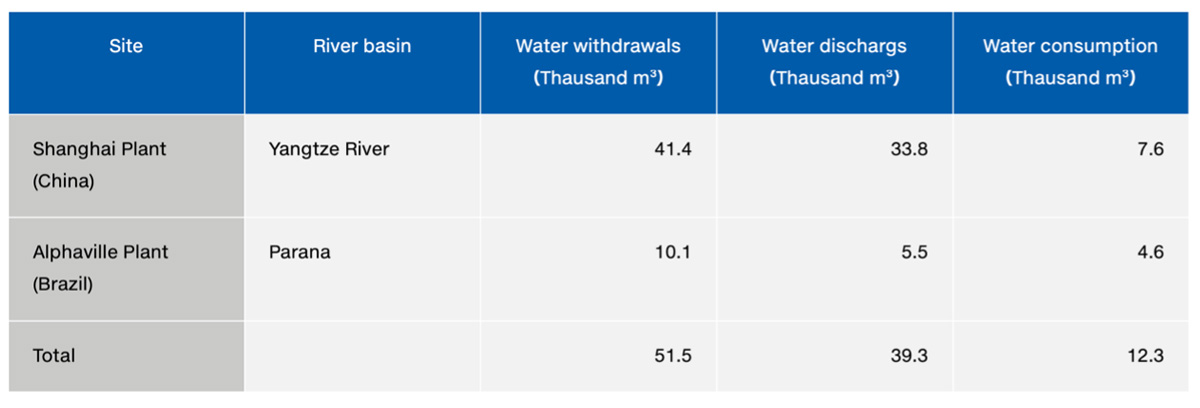
Specifically, we carry out comprehensive risk evaluations based on local water risk analyses using the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF)-DEG Water Risk Filter (Note 1) and the survey results on water risks gathered from plants and research facilities. These evaluations identified the Shanghai and Alphaville plants as being located in areas of highest water risk within the Group. Key risk factors include restrictions on water withdrawal and the tightening of related regulations (Fig. 1). Although these plants currently contribute less than 5% to the Group’s overall sales, they remain vigilant regarding regulatory developments and are actively working to further optimize water usage. Specifically, the Shanghai plant utilizes recycled water for sprinkling, while the Alphaville plant uses rainwater for domestic purposes.
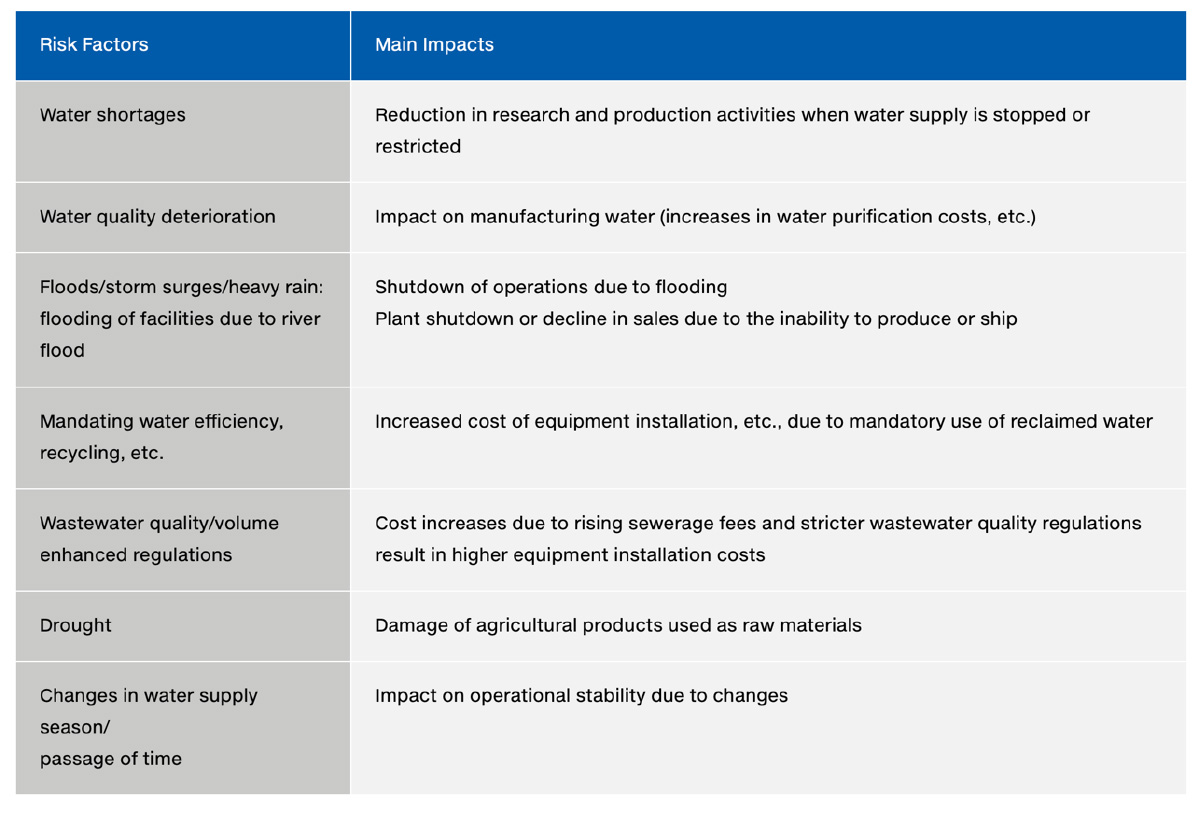
In Japan, the Daiichi Sankyo Group seeks to understand the potential impact of physical, regulatory, and reputational water-related risks—such as water quality degradation, water shortages, restrictions on effluent quality and volume, and the need for efficient water use—through questionnaire-based surveys. Based on the findings, we continue to analyze and evaluate these risks (Fig. 2). In addition to initiatives such as reducing industrial water consumption at domestic plants, measures were taken in FY2022 to address the growing severity of climate-related disasters. These included flood risk assessments, the development of water damage countermeasure manuals, and plans for flood mitigation measures at the Shinagawa and Kasai R&D Centers. We also completed flood risk measures at our domestic research laboratories and manufacturing plants, having confirmed that the risk of flooding is extremely low at the Onahama Plant of Daiichi Sankyo Chemical Pharma and the Kitamoto Plant of Daiichi Sankyo Biotech.
To address the physical risk of temporary shutdowns at our facilities due to flooding, we have set a goal of achieving “100% coverage of water disaster response manuals at all research laboratories and production sites in Japan by FY2025”. As part of this initiative, risk assessments and the development of site-specific water disaster manuals were completed in FY2023. Furthermore, the company’s data on water consumption and wastewater discharge is assured by an independent third party.
Effects/Expected Benefits
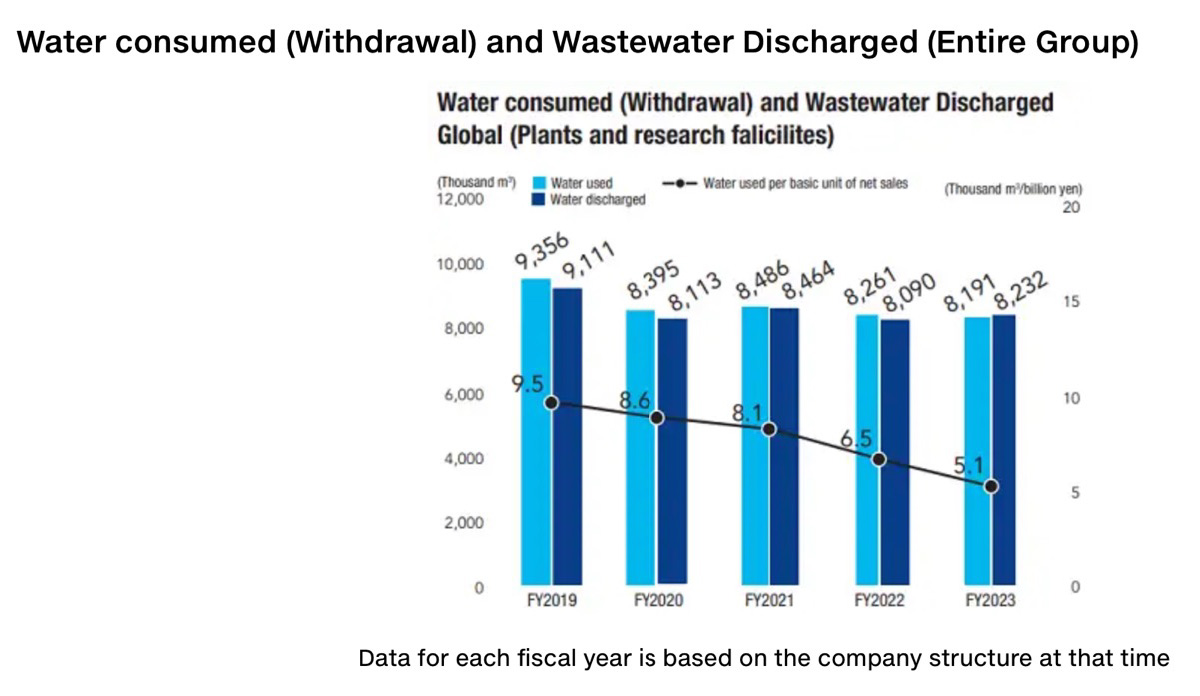
Through the appropriate use of water resources, the water consumed per unit of net sales in FY2023 was 511m³/ billion yen (down 40.7% from FY2020); while the total volume of water used by the entire Group was 8,191 million m³ (down 2.4% from FY2020) (Fig. 3).