Climate change impacts
The average temperature in Germany is currently 1.3°C higher compared to 1881, and extreme weather phenomena have been increasing in recent years, including severe flooding in 2013, an extremely dry summer in 2015, and flash floods in the spring of 2016.
Adaptation activity
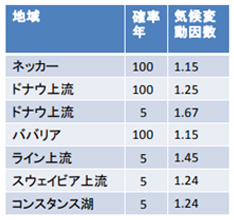
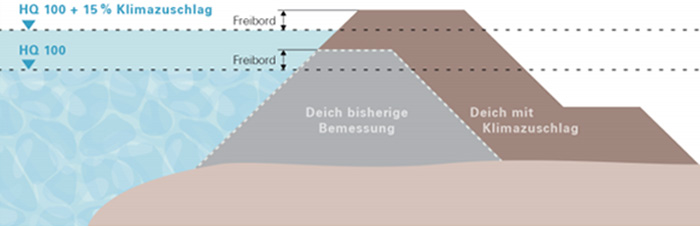
In order to better understand climate-change impacts on the water balance of river basins in southern Germany and to make policy recommendations, joint KLIWA projects were launched in 1999 by the states of Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, and Rhineland-Palatinate and the German Meteorological Agency. Simulations based on water balance models of river basins in three states predict that flood flow (see Note 1) levels will continue to increase in almost all regions, especially in winter. From the early 2000s, revised flood protection facility plans calculate flow by multiplying the impact of conventional flows according to climate change factors. Climate change factors are set by region and by flood scale (see Table). For example, the factor in the Necker region is 1.15 with a 100-year probability, which would take into account a 15% increase in flow rate over the present in case of a flood with a probability of once in 100 years. The levees should be constructed as planned, and the surrounding area should be secured so that the levees can be easily raised and widened when necessary (Fig.). Bridges are designed to accommodate flow rates that take into account climate change factors, and retaining walls are designed to be easily raised as needed.
Outputs / Expected benefits
In the past, joint KLIWA projects focused on flood-related problems and addressed these issues, but today the focus has shifted to the impact of low-water flow (Note 2), groundwater, heavy rain control, and water ecology. It also focuses on extreme short-term increases in precipitation.
Footnote
(Note 1) River flow rate during a flood.
(Note 2) One of the indicators of a river flow condition is that the flow rate does not drop below the river’s nominal level for 275 days of the year.