Climate change impacts
The Colorado River system in the United States spans seven states and provides millions of residents and tourists with water, food, recreation, and electricity. However, changes in climate conditions have resulted in a decrease in the water supply as a result of increased demand.
Adaptation activity
In 2010, the U.S. federal government and stakeholder state governments, through joint research on river flow and water usage, reviewed supply and demand scenarios for the geographically and socially complex Colorado Basin to address potential issues in the next 50 years. The Colorado River Simulation System (see Note) was introduced in a study led by the United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR), and more than 100,000 simulations were run using statistical software and visualization tools. The results were publicized with an online seminar given by the government's joint research team, which explored a variety of ideas to reduce risks and vulnerabilities, organized into 30 strategies. For example, measures such as increasing supply, reducing demand, improving reservoir operation, and changing management regulations for water use have been proposed.
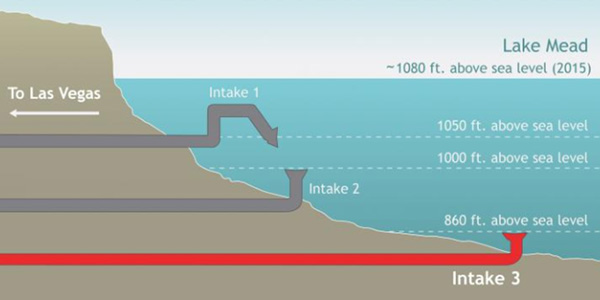
The Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) invests heavily in combating the effects of global warming, such as reduced snow cover, and low water levels in the Colorado River. Before the release of the 2012 study by the USBR, the SNWA started construction of a new intake pipe that can draw water from Lake Mead even when water levels are low (Fig.). The joint research indicated that vulnerability can be reduced by 50% if aggressive measures to manage existing infrastructure, regulations, and water use, such as those taken by the SNWA, are adopted.
Outputs / Expected benefits
In 2013, the USBR launched the ‘Moving Forward’ program to promote collaboration and dialogue on complex hazard mitigation decisions for the vast area of the Colorado River Basin. The program assists in policymaking with regards to increasing the resilience of the water supply across the basin by providing data and research. Quantitative data and information of realistic future scenarios are critical to facilitating effective action now, in order to prompt policymakers' interest in developing resilience in the immediate future.
Footnote
(NOTE) Method of investigating potential impacts of river operations and projected water supply and demand.