Countermeasures Against Heat Exhaustion at Work Sites with Highly Breathable Chemical Protective Clothing
Toray Industries, Inc.
| Publication date | May 20, 2021 (Posted on May 30, 2022) |
|---|---|
| Sector | Human Health |
Company Overview

Toray Industries, Inc. is a manufacturer, processor and marketer of fibers, functional chemicals, carbon fiber composite materials, environmental and engineering products, and life science products.
Climate Change Impacts
Chemical protective clothing is usually made of dense materials or laminated with films to prevent dust and liquids from entering. However, the breathability will be compromised in that case, which increases the temperature and humidity inside the garment, especially in summer or in hot environments, causing the risk of heat stroke among workers. It is concerned that further rise in temperature due to climate change will increase the risk of heat stroke.
Adaptation Initiatives
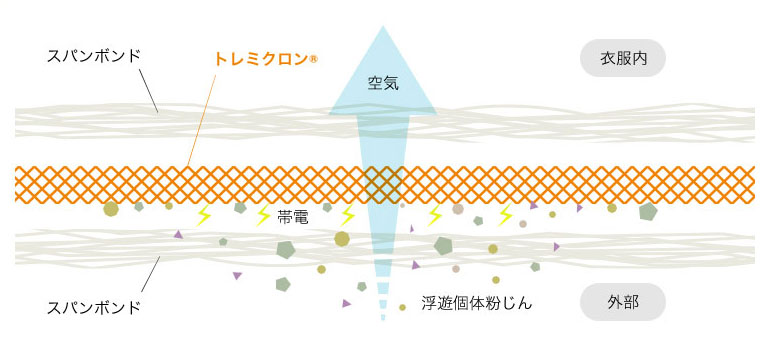
Our chemical protective clothing LIVMOA® highly breathable type (Fig.1) uses electrostatic non-woven fabric used in air purifiers to prevent fine dust particles from coming through the electrically charged layer while maintaining high air breathability (Fig.2). While it complies with the JIS T 8115 chemical protective clothing type 5 (airtight clothing for protection against suspended solid dust) standards, the unprecedented high air permeability of 96 cc (Note 1) reduces the temperature and humidity inside the clothing by a maximum of 31% (Note 2). The reduction in the temperature and humidity inside the garment leads to a reduction in the risk of heat stroke for workers wearing the product.
Footnote
(Note 1) Approximately 0cc to 30cc of other products (based on our survey).
(Note 2) LIVMOA® reduced the humidity inside clothes by up to 31%Rh when stepped on, compared to other products.
Effects / Expected Benefits
Since safety must be prioritized in work sites where chemical protective clothing is worn, effective heat countermeasures are still few. In this context, we are expecting that the prevalence of LIVMOA® highly breathable type will reduce the risks of heat stroke for as many workers as possible.