Footnote
(Note 1) OT (Operational Technology). Defined here as hardware and software technologies that monitor and control physical equipment and processes. This refers to the “control and operational technology” that optimally run essential equipment and systems for the operation of social infrastructure, such as electricity, railways, iron and steel, water, and industrial plants.
(Note 2) IT refers to information technology. It is a generally used term for technologies that utilize a combination of communications such as the Internet and information devices such as computers.
Image Analysis Technology that Uses AI to Recognize Disaster Situations
Hitachi, Ltd.
| Publication date | August 22, 2022 (Posted on June 5, 2023) |
|---|---|
| Sector | Natural Disasters / Coastal Areas |
Company Overview

Since its founding, Hitachi has responded to the expectations of society and customers through innovation based on its corporate philosophy of "to contribute to society through the development of superior, original technology and products.” By integrating control and operational technology (OT) (Note 1), information technology (IT) (Note 2), and products, we are engaged in creating new values and resolving social issues.
Climate Change Impacts
In recent years, many regions around the world have experienced massive damage from natural disasters associated with climate change due to global warming and urbanization. Japan has also incurred enormous damage from large-scale floods, landslides, and the destruction of buildings, having suffered a series of disasters of its own, including the torrential rainstorms in western Japan in 2018.
When a disaster occurs, it is a matter of urgency for rescue teams to rapidly identify disaster sites and provide evacuation guidance to victims. After the disaster had occured, it is necessary to accurately assess the state of the affected area, including knowing if there are blocked roads or collapsed bridges that requires restoration.
Adaptation Initiatives
Utilizing our expertise we have accumulated in video analysis technology for crime prevention and manufacturing sites, we have developed a technology that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze images of stricken areas captured by unmanned aerial vehicles with high accuracy (Fig. 1). This technology has the following four features.
- Possible to accurately recognize targets with high precision even when the captured image contains multiple objects such as water, houses, etc. (Fig. 2).
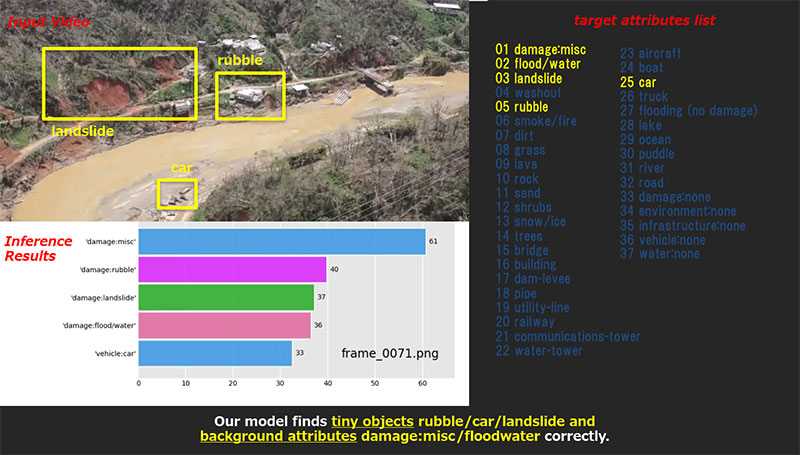
- Capable of recognizing small objects that are difficult for people to find visually from the wide range of captured images (Fig. 3).
- Even for disaster data with a small number of training samples, high-precision recognition can be obtained by training the AI to focus on the samples (Fig. 4).
- Even for disaster situations that are difficult for humans to assess, AI learning methods for training samples that contain many incorrect information can reduce actual misrecognition and missed information in the event of a disaster (Fig. 5).
This technology achieved world-class recognition precision at the “Disaster Scene Description and Indexing”, hosted by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. and held from April to July of 2020.
Effects / Expected Benefits
In cases when an earthquake, flood, or other large-scale event affects a wide area, the use of this technology makes it possible to analyze aerial images captured by drones and to find, with pinpoint accuracy, locations where rescue operations should immediately be directed.
After a disaster, insurance companies will also dispatch adjusters to the affected area to survey the damage.
Together with local governments and our various partner companies, we plan to disseminate this technology with the hope to increase lives saved during a disaster and contribute to a safe and worry-free ways of living.