Worker Safety and Health Management System with Pulse Monitoring
TOBISHIMA CORPORATION
| Publication date | March 30, 2021 (Posted on July 13, 2022) |
|---|---|
| Sector | Human Health, Industrial and economic activities |
Company Overview

TOBISHIMA CORPORATION celebrated its 138th anniversary in 2021, since Bunjiro Tobishima founded Tobishima-gumi, a civil engineering contractor, in Fukui Prefecture in 1883.
Since the foundation, we have developed a variety of original technologies associated with construction and have responded to social needs such as disaster prevention and environmental preservation, with our technological capabilities backed by our history of involvement in social infrastructure development projects in Japan and overseas. Today, the evaluation of corporate value is rapidly shifting to an assessment that adds the "degree of contribution to the realization of a sustainable world" to financial performance, and we our strengthening our efforts to address the SDGs and aiming to be a trusted company and a “chosen company” for our stakeholders. We are also widely expanding our original technology and expertise within and beyond the construction industry.
Climate Change Impacts
Research and development on monitoring vital data, such as the pulse rate and body temperature of on-site workers, have been promoted in the recent years from the viewpoint of improving the safety of construction work. In the construction industry, the number of occupational accidents is higher than in other industries, and the aging of technicians is advancing, also the occurrence of occupational accidents due to health such as heat stroke is also increasing.
Adaptation Initiatives
To improve the safety of construction work, we have developed a safety and health management system that can constantly monitor the health conditions of workers at work sites in order to manage their physical conditions and prevent illnesses such as heat stroke.
Many of the vital data monitoring systems developed so far for construction work use mobile phones (smartphones) provided to the workers. However, this method requires each worker to carry a phone, and the manager to be responsible for them. In order to reduce the burden on the workers and managers, we have developed a spot-type gateway system in which a common gateway device is installed at places where work is concentrated to be shared for use.
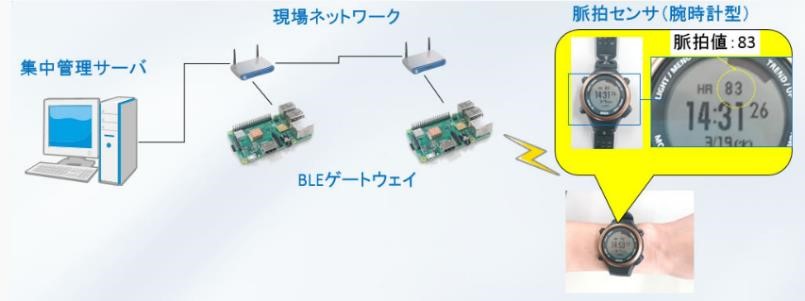
The system includes a wristwatch-type sensor that collects pulse data (Fig. 1), a server that aggregates the data, and a gateway device that links the two (Fig. 2). For the gateway, a device with BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and wireless LAN was adopted because wireless LAN transmission device is commonly used in tunnels where mobile phone network could be an issue.
The pulse sensors worn by each worker constantly measure the pulse, and the gateway device regularly collects the results of the workers near the gateway and transmit the data to the server. The server then centrally manages user names, current user location, and pulse rates based on the pre-registered information of the pulse sensor, user information, gateway, and the location where the gateway is installed.
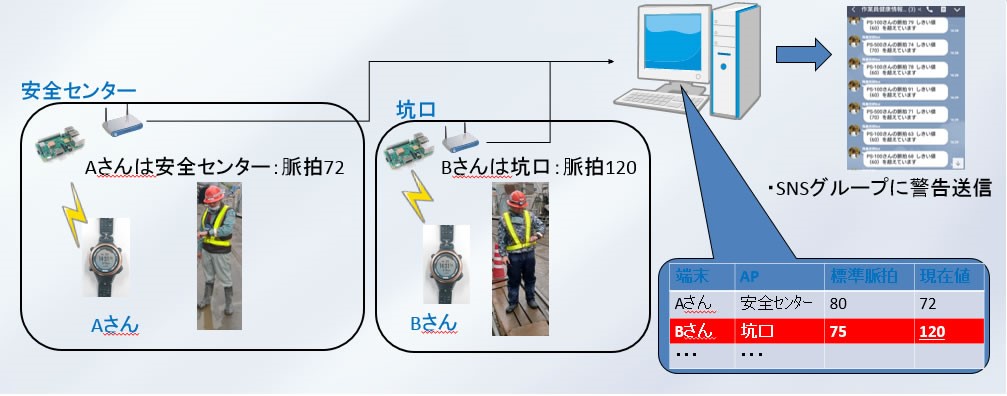
The system can determine the real-time location and pulse rate of the users. When the pulse rate exceeds the pre-set value, the system has a function to send warning information to the group chat of a social media application (Fig. 3).
The system was tested in a tunnel construction project to verify the effectiveness, and it was verified on site that it was possible to constantly monitor the pulse of the workers which fluctuates according to the work load. However, the data collection rate decreased when there was an obstacle between the spot-type gateway and the pulse sensor, and we found that the placement of the spot-type gateway needs to be carefully decided in the actual operation.
Effects / Expected Benefits
Until now, our health management of workers has been limited to qualitative evaluation such as visual observation by managers, but this system will enable quantitative and detailed management. We expect this system to be effective in managing the physical conditions of the on-site workers and preventing illnesses including heat stroke.

- TOBISHIMA CORPORATION, Tobishima Technical Report No. 67 (2019), Measurement and Construction Management System "06. Development of Heart Rate Monitoring Spot-Type Gateway"
- TOBISHIMA CORPORATION, Technology of TOBISHIMA CORPORATION “Quantitative Evaluation of Worker's Health Conditions from the Pulse Rate: Safety Management System Based on Pulse Rate Monitoring”

