Footnote
(Note 1) Based on published reports as of October 22, 2021.
(Note 2) Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: cross-sectoral socioeconomic scenario used in climate change research.
(Note 3) Population data is based on "Japan Shared Economic Pathways Population Estimates by Municipality" by the National Institute for Environmental Studies, and GDP data is based on "Global Dataset of Gridded Population and GDP Scenarios" by IIASA (International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis).
(Note 4) Rainfall of a scale that is expected to occur once in 10 to 100 years.
(Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Hazard Map Portal Site:
https://disaportal.gsi.go.jp/hazardmap/faq/faq.html#kasaneru5)
(Note 5) Hirabayashi Y. et al. 2013. Global flood risk under climate change. Nature Climate Change, 3 (9), pp. 816-821.
(Note 6) RCP (Representative Concentration Pathways): Representative Concentration Pathway Scenarios used in the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
(Note 7) SJR East Group Report 2021, p. 19, "Initiatives to address flooding";
https://www.jreast.co.jp/e/environment/pdf_2021/all.pdf
Strengthening and Promoting Initiatives to Reduce Physical Risks in the Transportation Services
East Japan Railway Company
| Publication date | July 27, 2022 (Note 1) |
|---|---|
| Sector | Industrial and economic activities |
Company Overview

Since its establishment, East Japan Railway Company has pursued the rehabilitation and revitalization of railways, expanding its business into fields such as Life-style and IT & Suica services. In 2018, we announced our group management vision "Move Up” 2027, and set out a basic policy to evolve our “railway-based” business model by adopting "people-focused" approach and to promote new growth strategies.
Climate Change Impacts
We have formulated our management vision, "Move Up" 2027 to pursue "ultimate safety" by focusing on various risks that threaten safety, such as extreme weather conditions and severe disasters (strong wind, torrential rain, etc.); we are promoting the achievement of the SDGs by implementing ESG management practices and proactive disclosure of information using the TCFD framework. In particular, the extensive damage caused by Typhoon No. 19 in October 2019, which resulted in flooding damage and suspension of the bullet train service, reinforced our recognition of the importance of disaster preparedness.
Adaptation Initiatives
The risks and opportunities associated with climate change include those that result from physical changes, such as severe weather caused by global warming, and those that result from transitions, such as strengthened regulation and technological progress in the process of decarbonization.
Based on the results of the assessment of the main climate change risks and opportunities (Fig. 1), we have targeted "damage to railroad facilities and equipment and suspension of operations due to wind and water disasters" in the transportation service business. Targeting the year 2050, we conducted scenario analysis to understand passenger revenue trends based on demographics and the financial impact of natural disasters, and to verify the appropriateness of our business strategy. A summary of the analysis is provided below.
(1) Estimated change in of passenger revenue trends based on business are demographics
Based on population data from the SSP (Note 2) and GDP (Note 3) (Fig. 2) , we estimated passenger revenue trends up to 2050, taking into account the outlook after the COVID-19. As a result, there will be a difference of approximately 11% in the population estimate and approximately ¥350 billion in the estimated passenger revenue in 2050 between the scenario of “Sustainability” (SSP1) that we are aiming for, and the opposing scenario of “Regional Rivalry” (SSP3).
(2) Estimated of physical risk caused by natural disasters
The majority of our major railway assets and lines with significant passenger revenues are concentrated in and around the Tokyo metropolitan area. Therefore, we selected a flooding scenario of the Arakawa River which is assumed to have the greatest financial impact in the event of a disaster in this area, based on estimated rainfall scale (Note 4). We used the inundation assumptions published by the government, the asset values of major lines, passenger revenue trends, and the increase in the future flood probability (Note 5), to quantitatively evaluate the financial impact up to 2050. As a result, in the single year of 2050, the financial impact in the RCP2.6 (2°C) scenario (Note 6) is expected to increase by ¥3.4 billion, and the financial impact in the RCP8.5 (4°C) scenario is expected to increase by ¥4 billion, including the decrease in passenger income and increase in disaster recovery costs.
Effects / Expected Benefits
JR East is promoting both hardware (physical facilities) and software (human responses) countermeasures against natural disasters according to the importance of the facilities, such as raising the height of electrical equipment that are expected to have a critical impact on operations, installing water stop plates at building openings, and developing a Vehicle Evacuation Judgement Support System and Vehicle Evacuation Manual (Note 7). When these effects were taken into account in the scenario analysis, the increase in financial impact was ¥1.3 billion under the RCP 2.6 (2°C) scenario and ¥1.6 billion under the RCP 8.5 (4°C) scenario (Fig. 5), confirming the effectiveness of our countermeasures.
We will continue to estimate the financial impact of other major scenarios and confirm the effectiveness of our countermeasures.

Fig. 1 Identification and assessment of risks and opportunities
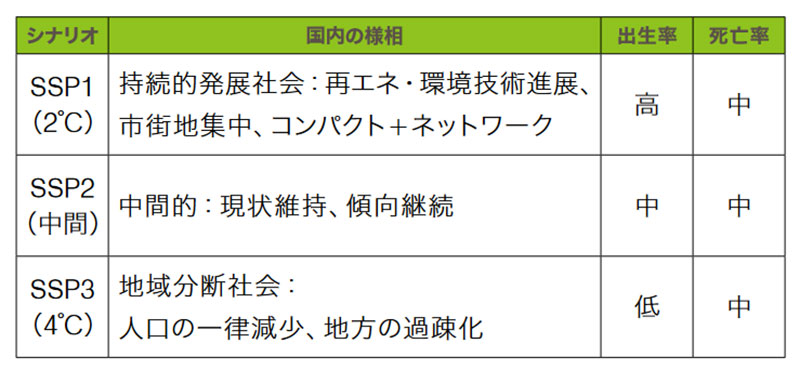
Fig. 2 SSP settings
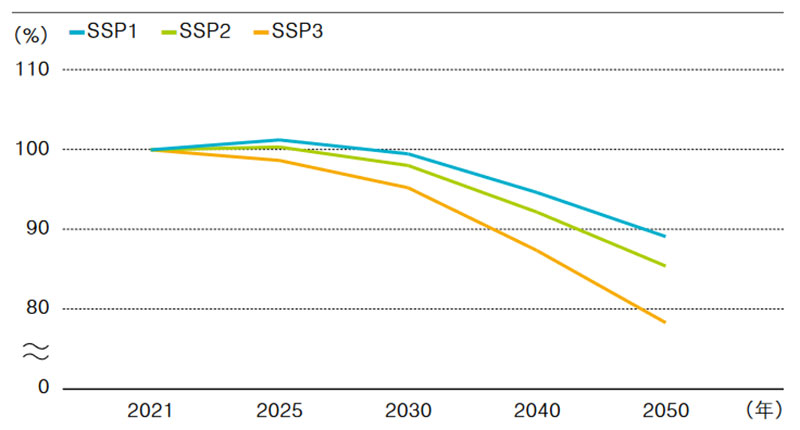
Fig. 3 Business area population estimates by scenario
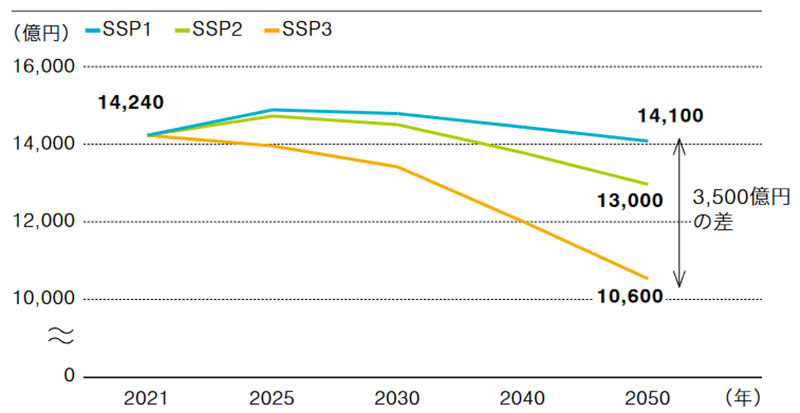
Fig. 4 Trends in passenger revenue by scenario
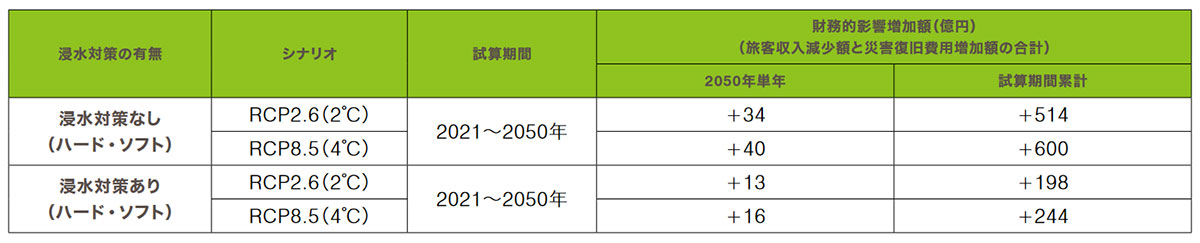
Fig. 5 Effects of natural disaster countermeasures

