Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
YAMATO HOLDINGS CO., LTD.
| Publication date | June 15, 2023 (Posted on May 13, 2024) |
|---|---|
| Sector | Industrial and Economic Activities |
Company Overview

Established in 1919, YAMATO HOLDOINGS CO., LTD. is the holding company for the Yamato Group, which includes the transportation company Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. The group operates various transportation businesses, including TA-Q-BIN, as well as various transportation-related service businesses within and outside of Japan.
Climate Change Impacts
In order to realize sustainable management, it is necessary to analyze the impact of climate change, identify and recognize risks and opportunities, and incorporate countermeasures into our medium- and long-term plans to achieve sustainable business growth. Short-term risks from climate change include physical risks such as business shutdowns due to more severe and more frequent extreme weather events, and increased repair costs due to damage or loss of facilities and equipment. Medium- and long-term opportunities and risks include increased capital investment to adapt to climate change and increased costs such as carbon taxes, but we also expect that proactive efforts to reduce environmental impact will lead to customer acquisition opportunities.
Adaptation Initiatives
The Group recognizes that identifying the risks and opportunities that climate change related issues pose to society and the company, assessing the impact, and developing countermeasures are essential for business sustainability. Based on the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD), we conducted a scenario analysis for Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. in FY2021, and in September 2022, announced our support for the TCFD recommendations and disclosed the information in November of the same year.
In the scenario analysis, STEP 1 was to understand the situation regarding risks and opportunities, STEP 2 was to define the predicted climate scenarios, STEP 3 was to assess the impact on business based on the scenarios, and STEP 4 was to define countermeasures against the impact. The results of the analysis of climate change adaptation are described below.
- STEP1 Risks severity assessment
We categorized transition and physical risks, analyzed the level of importance of the risk/opportunity, and its assumed time period (Fig. 1, *1 and *2).
- STEP2 Definition of scenarios
For scenario analysis, the Group assumed two scenarios (1.5℃ scenario and 4℃ scenario; if an item does not have a 1.5℃ scenario, see a 2℃ scenario) for Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. in FY2021 based chiefly on information from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) (Figs. 2 and 3,*3).
- STEP3 Evaluation of Business Impact
In FY2021, the Group assumed that of the selected risks, the introduction of carbon tax and extreme weather and disasters may particularly cause significant impacts on revenue and expenses and conducted the analyses and business impact assessments below.
- Financial impact assessment due to introduction of carbon tax
We calculated the business impact of a full-scale introduction of carbon tax in 2030 and 2050. We assumed that carbon tax will be $130/t in 2030 and $250/t in 2050. Based on the assumptions, the impact of carbon tax on Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. will be 13.3 billion yen in 2030 and 25.6 billion yen in 2050. - Financial impacts of extreme weather and disasters, that is, a decrease in revenue and an increase in facilities and equipment repair cost
We estimated the business impact—that is, a decrease in sales and the cost of repairing facilities and equipment (*4)—of extreme weather such as severer typhoons and heavy rains caused by linear precipitation zones. The business impact is estimated at 1.9 billion yen in 2030 and 3.8 billion yen in 2050.
- Financial impact assessment due to introduction of carbon tax
- STEP4 Direction of countermeasures
- Introduction of carbon tax
The Group strives to reduce GHG emissions, setting an ambitious goal of reducing its own emissions to carbon neutrality in 2050. Specifically, we aim to reduce GHG emissions by 48% from FY2020 by FY2030. The main initiatives to achieve this goal include introducing 20,000 electric vehicles and installing 810 solar power systems by FY2030. In addition, up to FY2050, we will implement other initiatives, including introducing cartridge battery EVs (BEV(*5)) and other low-carbon vehicles and installing additional solar power systems. We are also considering the introduction of internal carbon pricing (*6) to promote capital investment to reduce carbon emissions. - Increase in the cost for repairing facilities and equipment
In addition to making good use of hazard maps when opening sales offices and updating the BCP manual regularly, the Group is considering disseminating information about adapting to climate change in the Group and to the partners. We will also increase the usage of renewable energy to enhance resilience and conduct demonstrations of usage models for cartridge BEVs.
- Introduction of carbon tax
Effects / Expected Benefits
The assessment of risk and financial impact based on scenario analysis has enabled us to determine the direction of response measures. We will continue to assess the business impact by adding assumptions such as the location and the scale of the disaster. In addition to continuing and accelerating the implementation of response measures, we will also continue to address the direction of other risk and opportunity items as management issues.
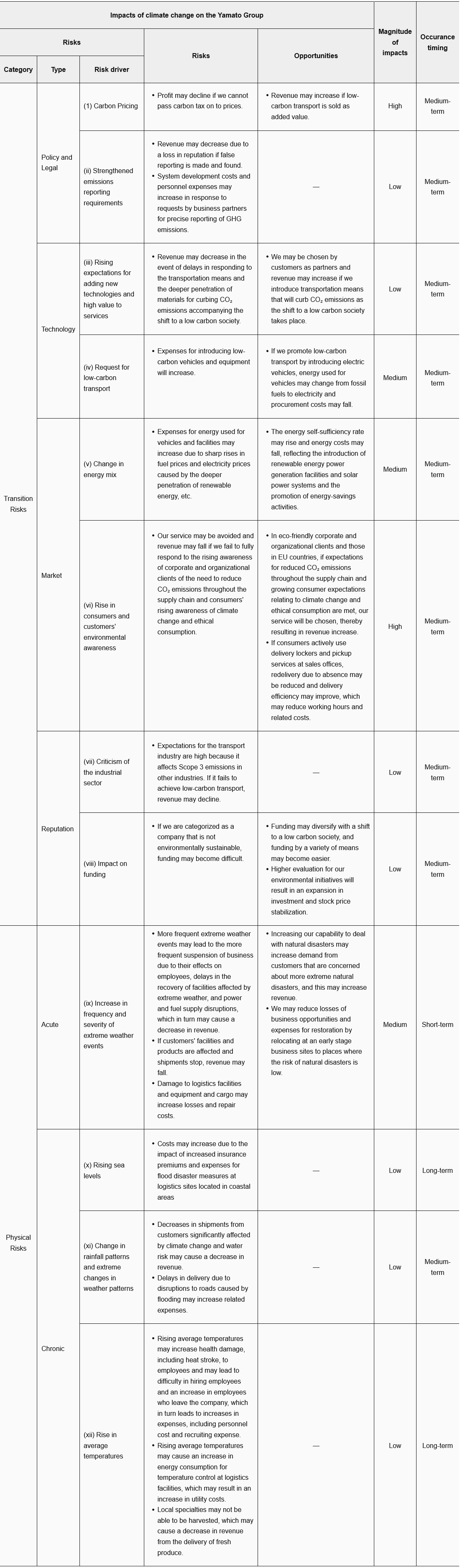
Fig. 1 Assessment of risk importance
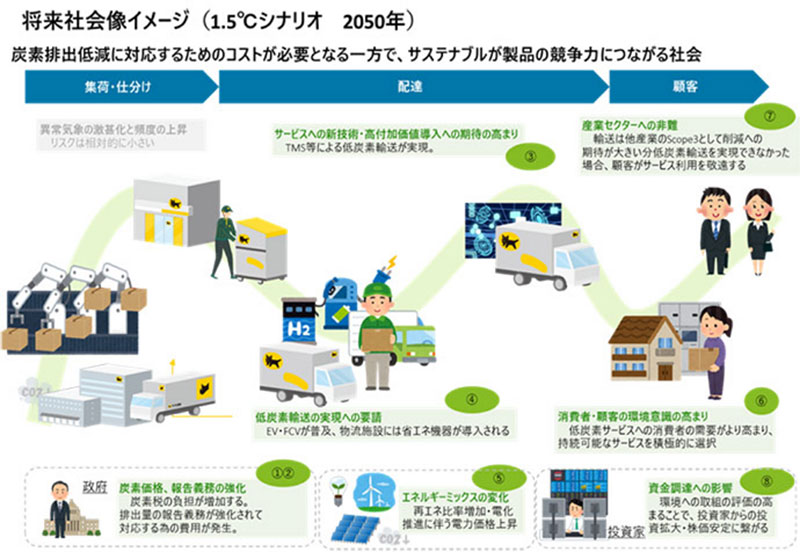
Fig. 2 1.5°C scenario, image of society in 2050
(① to ⑫ correspond to the subcategories in Fig. 1)
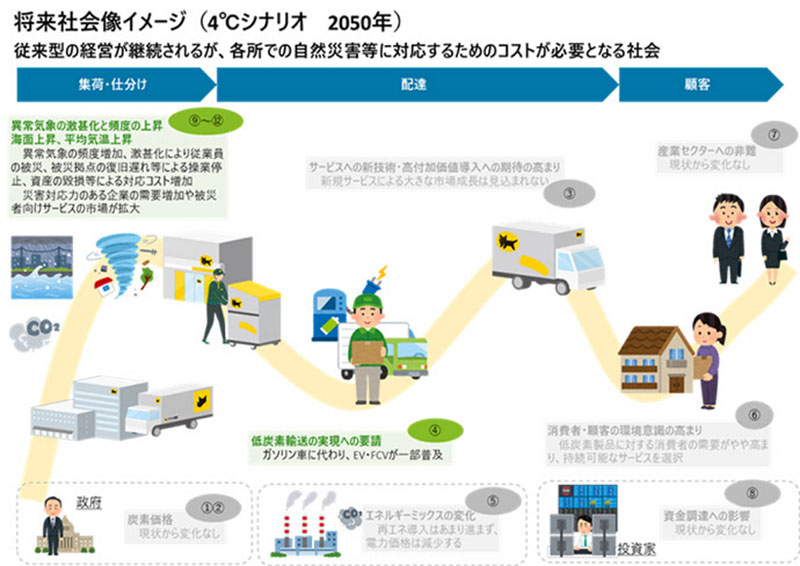
Fig. 3 4°C scenario, image of society in 2050
(① to ⑫ correspond to the subcategories in Fig. 1)
Notes
(*1) [Criteria for evaluating the magnitude of impacts]
The Group has set three levels of severity (high, medium, low) based on criteria for evaluating financial impacts on annual revenue and expenses.
High: 10.0 billion yen or more / Medium: 1.0 billion yen or more and less than 10.0 billion yen / Low: less than 1.0 billion yen
(*2) [Occurrence timing]
Short-term (up to 2023) / medium-term (2024 to 2030) / long-term (after 2030)
(*3) IPCC: RCP8.5, IEA: Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, Sustainable Development Scenario, and Stated Policies Scenario.
(*4) Estimated by reference to past disasters.
(*5) Cartridge-type battery electric vehicle. The use of removable and portable cartridge batteries eliminates the need for long recharging times. The company is examining ways to contribute to electric energy supply communities (resilience), such as delivering cartridge batteries in times of disaster or in areas where it is difficult to maintain electric power infrastructure.
(*6) A price of carbon estimated internally by a company, and a mechanism to promote low-carbon investment and measures by companies.

